Mark your calendars for our first-ever live debate! Tony Redmond and AvePoint’s John Hodges will debate “The Need for Office 365 Backup” on October 7th. Reserve your free spot here.
There’s no question that where there’s valuable data, there’s the need to keep it protected. OneDrive for Business is Microsoft 365’s cloud storage solution that lets business users access and share documents from anywhere via the cloud.
Though that ease of access is incredibly convenient and there are powerful data protection tools in Microsoft 365, data loss events still happen. Incidents like accidental deletion, malware infestations, and file corruption are still situations for which to prepare.
If you’re an end user who is about to throw their laptop out the window because of hours of lost work from a file you can’t locate or if you’re an Office 365 admin considering backup strategies around OneDrive, this blog post is for you.
First, let’s walk through some of the native restore options and strategies.

Native Office 365 Backup and Restore Options
File Restore
True to its name, OneDrive for Business File Restore is an out-of-the-box recovery solution that end users and admins alike can leverage to restore files lost any time over the last 30 days.
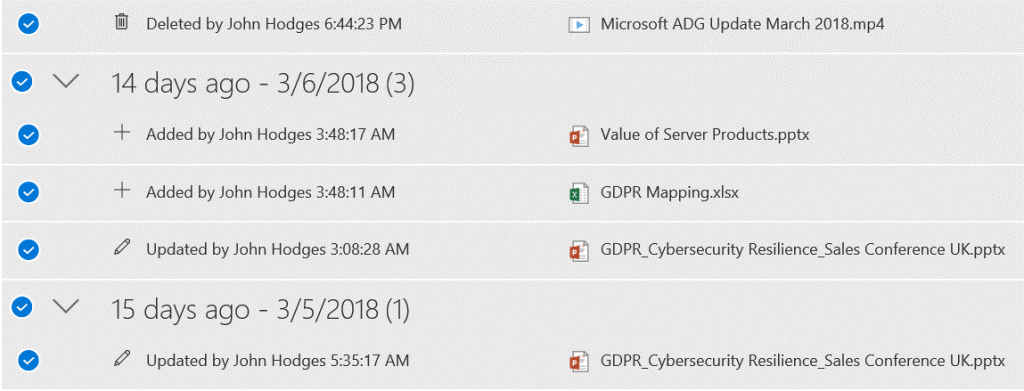
Even the smallest changes to files and folders can be inspected within that timeframe to ensure no foul play was afoot relating to the data loss. No matter if a file was corrupted, accidentally (or intentionally) deleted, or overwritten, you have the tools to restore it as part of your Microsoft 365 subscription.
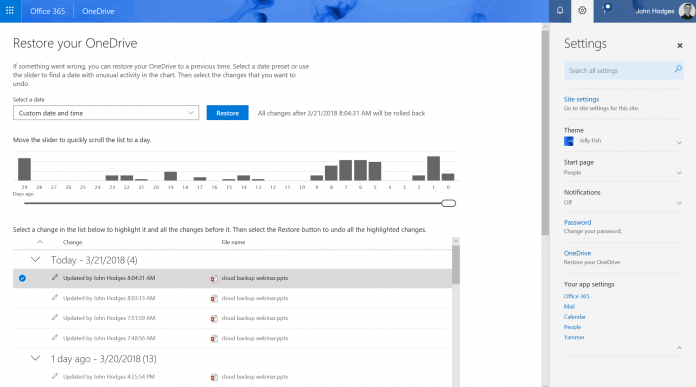
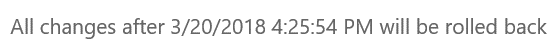
User and admin beware: you are not restoring an individual file as you may expect. Instead, you’re actually restoring to a previous point in time within your OneDrive. This means that any changes and work you have done from that point will be reverted as well (and there isn’t an undo button).
Any time you have to rely on a broad rollback (entire Sites, OneDrives, Mailboxes, etc.) you will face an end-user impact.
File Restore also leverages version history, so if that’s turned off (perhaps an admin is trying to save storage space), those files cannot be restored to a previous version.
Recycle Bin
You can also restore deleted or early versions of files directly from the OneDrive recycle bin. This is perhaps the most end user-friendly option; all it takes is a couple clicks and you can find exactly what you lost without having to waste resources by getting IT involved.
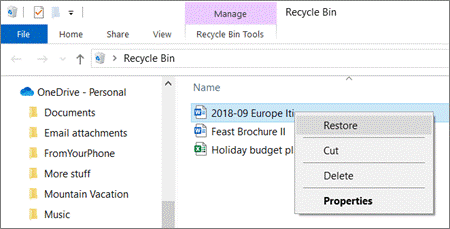
As long as this is done within 93 days of the deleted or altered file, you’re in the clear.
Microsoft Restore
If the OneDrive file was stored in a SharePoint site collection, there’s a secondary Recycle Bin that preserves the item for 14 additional days beyond the initial deletion. An admin can call Microsoft Support to try and restore the item within this window. Again, this only applies if the OneDrive file was stored within a SharePoint site.
Retention Policies
Some industry experts advise that Office 365 admins set broad retention policies to prevent all deletion and data loss (purposeful/accidental/benign/malicious). This has the benefit of enabling granular item restore capabilities if set ahead of the data loss event.
The limitations to a retention policy as OneDrive (or Office 365) backup strategy are that:
- When you keep everything, environments can get cluttered and lifecycle management can become an issue;
- Administrator error is still possible;
- Permissions (for Groups, Sites, Teams, etc) aren’t covered; and
- There is a significant cost to keeping all that data. Although the 1TB per user of OneDrive cloud storage in the Microsoft 365 Business Standard Plan is generous, data scales quickly when you’re keeping everything—especially if you’re dealing with large files. AvePoint’s Creative Director hit 800 GB and was on track for 1TB within 2 years of being at the company.
How to Empower Users To Restore Their Own Files Easily
AvePoint’s Microsoft Teams chatbot, AVA, is available for free in the Microsoft Teams store.
When Office 365 users accidentally delete—or can’t locate—files, documents, or emails, they won’t need to call IT. Instead, they can chat directly with AVA in Microsoft Teams. She will automatically perform a search based on the user’s permissions in Exchange, Outlook, and OneDrive’s recycle bin to restore the requested item (even if it’s out of place).
If your organization is an AvePoint’s Cloud Backup customer, AVA can also find content that’s no longer retained by Office 365’s native backup capabilities. For users who may not be savvy with finding or using features like File Restore or the Recycle Bin, AVA is a quick and easy way to restore files.

How to Extend One Drive for Business Protection
If you want to ensure that any potential lost files can still be recovered months down the line without retaining everything with a broad retention policy, investing in a third-party solution that can extend beyond what Microsoft provides out-of-the-box would be your best bet.
This is doubly true for backing up other Office 365 workloads like Teams, Planner, and SharePoint that contain items such as Planner tasks and permissions that native options don’t restore.
Not only do solutions like AvePoint’s Cloud Backup provide unlimited backup instead of cutting it off at 30 days, but it can also conduct multiple backups per day consistently. Configure your settings, schedule how often you want your files backed up, and it’ll do it automatically.
For as robust as Office 365 native backup and data protections are, sometimes you’re working in situations where you need a bit more coverage. If that’s you, we can’t recommend Cloud Backup enough.
If it’s not, I hope this post helped you understand the capabilities of OneDrive for Business File Restore a bit better. Finally, if you still have a question or two and want to pick our brains, feel free to drop a comment down below!


